Introduction
Molecular Recognition Features (MoRFs)
are short, intrinsically disordered regions in proteins that undergo a
disorder-to-order transition upon binding to their partners. MoRFs are
implicated in protein-protein interactions, which serve as the initial step in
molecular recognition.
The aim of this work was to collect,
organize and store all membrane proteins that contain MoRFs. We focused in
membrane proteins, as they constitute one third of fully sequenced proteomes
and are responsible for a wide variety of cellular functions. Data were
initially collected from Protein Data Bank (PDB) and Uniprot and were managed
with Perl scripts. MoRFs were classified according to their secondary
structure, after interacting with their partners. We identified MoRFs both in
transmembrane and peripheral proteins. The position of transmembrane protein
MoRFs was determined relative to a proteinÕs topology.
All information was stored in a publicly
available mySQL database with a user-friendly web interface. A Jmol applet is
integrated for vizualization of the structures. The utility of the database is
the provision of information related to disordered based protein-protein
interactions in membrane proteins. Such proteins play key roles in crucial
biological functions and ca. 50% of them are putative hubs in protein
interaction networks. Consequently, these proteins may be correlated with
various human diseases. The database will be updated on a regular basis by an
automated procedure.
Home Page
In order to visit mpMoRFsDB, user should enter one of the following addresses:
http://bioinformatics.biol.uoa.gr/mpMoRFsDB/ or http://bioinformatics.biol.uoa.gr/mpMoRFsDB/index.php. The page loaded (see below) contains general information about the
database and some statistics.

Browse data
In order to browse database information, user should press the browse
button. A form appears with multiple options.

The choices are:
á Search membrane proteins according to type.
o
Single-Spanning (Transmembrane)
o
Multi-Spanning (Transmembrane)
o
Peripheral
o
All the above
á Search proteins containing specific types of MoRFs. MoRFs are
seperated in four categories, according to their secondary structure upon
binding to their partner.
o
Alpha MoRF
o
Beta MoRF
o
Ireggular MoRF
o
Complex MoRF
á Search proteins according to MoRF length. The length varies between 10
and 70 residues.
á Search proteins based on protein name.
á Search proteins based on gene name.
á Search proteins based on organism.
á Search proteins based on Uniprot Accession.
á Search proteins based on PDB ID.
The search, based on protein name, gene name and organism does not
require specific words. For example if user enters the word ÒhomÓ, the result
is all proteins containg the word ÒhomÓ in the field organism.


All the above search fields can be combined in order to make the
search result as specific as possible.
For example if we make the following combined search:

We get only one protein with the specific characteristics.
![]()
Another example is to find all single spanning membrane proteins
containing MoRFs with length from 20 to 30 residues.

And the result is:

If we want to select all proteins containing beta or complex MoRFs, we
make the following selection:

And the result is:

Entries
When user fills the search fields and presses submit a new page appears,
with the list of proteins like the image below. It contains the Uniprot Accession number, the protein name, the organism, the protein length
and the type of protein.

Entry
When the user presses the View button he is redirected to the entry
page. The entry page contains information about the type and topology of the protein,
the total number of MoRFs as well as their position in the protein. Moreover a
Jmol Viewer is integrated for vizualisation of the proteins in 3D.

More specifically:
á In the top right corner user can find three buttons. FASTA, TXT and
XML. By pressing these buttons user can download the sequence in FASTA format,
all page information in text format or all information in XML format
respectively.
á The protein information available is:
o
Protein Name
o
Gene Name
o
Organism
o
NCBI taxonomy
o
Sequence
o
Sequence length
o
Uniprot Accession
o
Protein Type
o
Total number of MoRFs
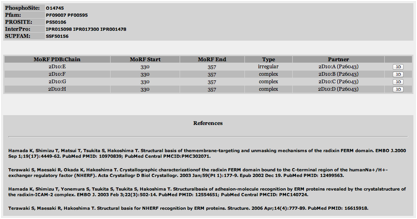
á The next box contains references to other databases. The databases
are:
o
Phosphosite
o
Pfam
o
Prosite
o
InterPro
o
SupFam
á The next box contains MoRF related information. It contains the MoRF PDB
ID and chain, where the MoRF starts and ends in relation to proteinÕs sequence and
the partner of the MoRF.
á The next box contains references related to the PDB IDs appearing in
the previous box.
á Last but not least a Jmol 3D viewer is integrated in the page for vizualization
of the structures. MoRFs are colored red. User can chose complexes by pressing
the Ò3DÓ button/s.
The topology of Single Spanning and Multi
Spanning proteins was determined as well as the position of MoRFs. In the
screenshot below user can view an example of topology (Uniprot Accession: P01730).
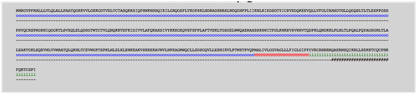
s: Signal
peptide
o:
Extracellular
i:
Cytoplasmic
M: Transmembrane
#: Position of MoRF
BLAST search
With the BLAST search tool, the user may
submit a sequence and search the database for finding homologues. The input for
the BLAST application is the sequence in standard FASTA format and the user has
the ability to specify an e-value cutoff level to use in the query:

The result page of the BLAST search shows a
list of the Blast hits with significant alignment on the query sequence the
user has submited. The list is in a table format including the mpMoRFsDB_ID
of the target protein, the Length of the target sequence and the Query
and Target align range. The BLAST results can be compared through the Score
and E-value and the Identities and Positives.
The result page of the above BLAST search
is:

Furthermore, the user can have a more
detailed view of each alignment through the Show/Hide button at the end
of each line:
Manual
User can view and downlad the current manual.
Download
User can download all database files in Text or XML format. The option
will be activated upon publication.
Contact
Users can contact us for more information at the emails specified at
the contact page. Related publications to the current work are also presented.
Technologies
mpMoRFsDB is based on modern technologies. User should have Javascript
enabled on the web browser. In order to use the Jmol Viewer user should also
have Java installed on his computer.




University of Athens
Faculty of Biology
Biophysics and Bioinformatics Laboratory
